Part:BBa_K2549043
CfaC-TEVpC
This part is one of the downstream elements of our amplifier. It is constructed by fusing CfaC (Part:BBa_K2549015) and TEVpC (Part:BBa_K2549010), from N terminal to C terminal. CfaC is the C-terminal fragment of Cfa which is a consensus sequence from an alignment of 73 naturally occurring DnaE inteins that are predicted to have fast splicing rates. TEVpC is the C-terminal fragment of TEV protease. TEV protease is one of the best-characterized enzymes of the viral proteases which have more stringent sequence specificity. When coexpressed with NLS-TEVpN-CfaN (Part:BBa_K2549042) in the same cell, two fusion proteins can form and the site-specific cleavage can be realized.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal BsaI site found at 91
Illegal SapI.rc site found at 21
Biology
Please visit http://2018.igem.org/Team:Fudan/Results and http://2018.igem.org/Team:Fudan/Measurement to check how we use this.
split TEV protease
MJ Rossner et al have demonstrated a biological assay termed split TEV. They engineered inactive fragments of the NIa protease from the tobacco etch virus (TEV protease) that regain activity only when coexpressed as fusion constructs with interacting proteins[1].
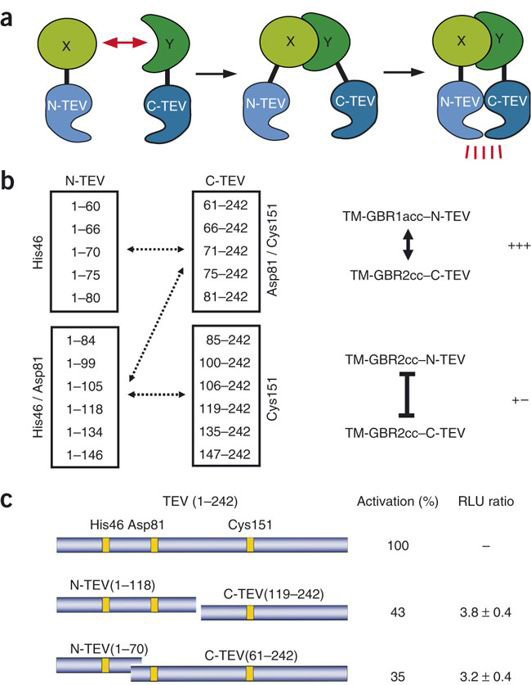
Thus in our split TEV protease assay, we chose site between 118 amino acid and 119 amino acid of TEV protease as the split site.
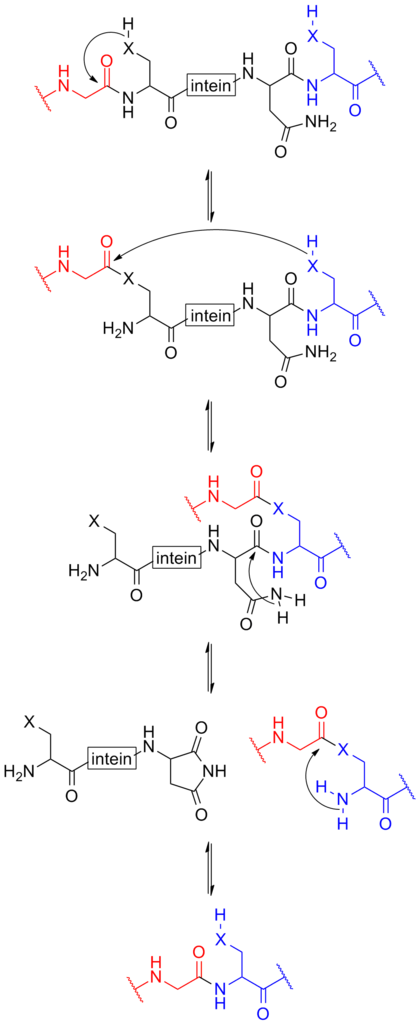
intein-based protein splicing
Schematic below provides a mechanism of how the intein function[2].
For more details about intein-based protein splicing, please refer to our CfaN (Part:BBa_K2549009) and CfaC (Part:BBa_K2549010).
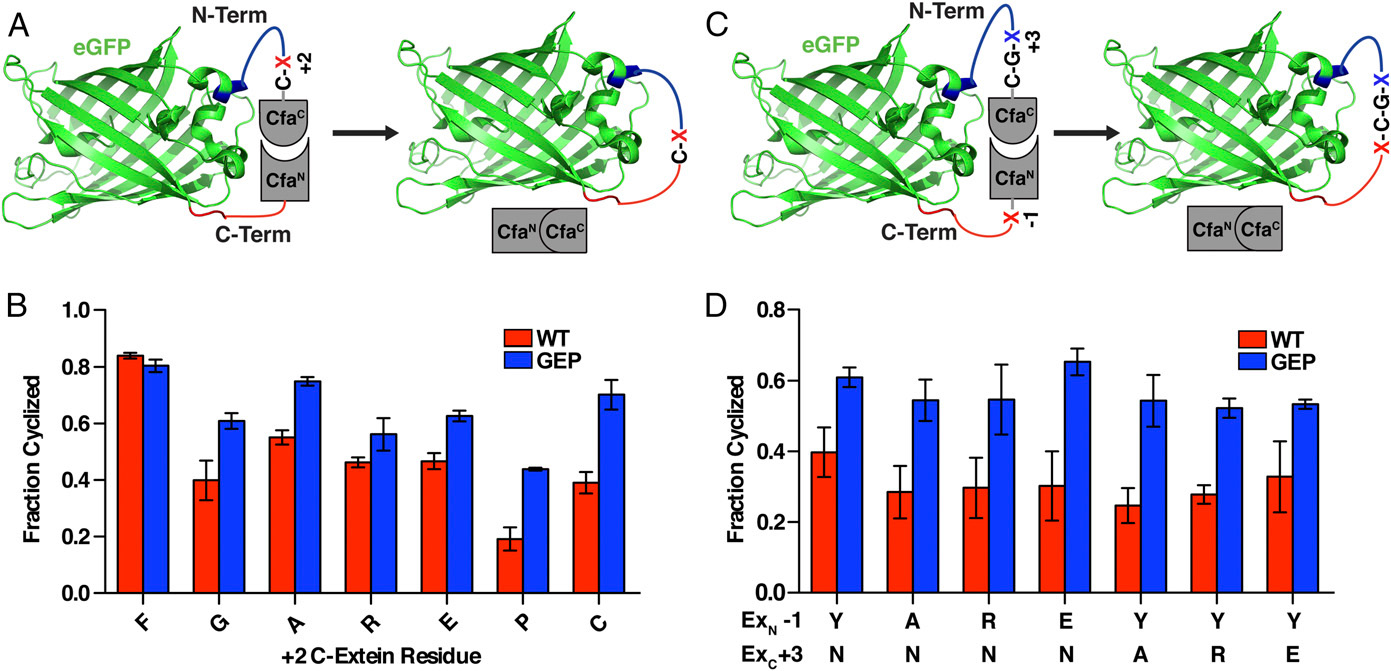
a three-amino acids sequence added to the original TEVpC
Extein sequence preferences are largely confined to the catalytic cysteine at the +1 position and large hydrophobic residues that are preferred at the +2 position of the C-extein[3]. The EKD to GEP mutation has drastically lowered the extein dependence of CfaC[4]. Even so, we have added a Cys-Ala-Glu sequence to the original C-terminal fragment of the TEV protease to achieve higher efficiency of cleavage.
References
- ↑ Monitoring regulated protein-protein interactions using split TEV. Wehr MC, Laage R, Bolz U, ..., Nave KA, Rossner MJ. Nat Methods, 2006 Dec;3(12):985-93 PMID: 17072307; DOI: 10.1038/nmeth967
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Intein
- ↑ Faster protein splicing with the Nostoc punctiforme DnaE intein using non-native extein residues. Cheriyan M, Pedamallu CS, Tori K, Perler F. J Biol Chem, 2013 Mar;288(9):6202-11 PMID: 23306197; DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.433094
- ↑ A promiscuous split intein with expanded protein engineering applications. Stevens AJ, Sekar G, Shah NH, ..., Cowburn D, Muir TW. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2017 Aug;114(32):8538-8543 PMID: 28739907; DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1701083114
//proteindomain/internal/special
| None |